Introduction
Terminology
Welcome to Infinitic! Understanding the key terms used in Infinitic is crucial for effectively utilizing its capabilities. This guide breaks down the essential terminology in simple terms, helping you get a clear picture of how Infinitic operates.
Services
Services are the backbone of Infinitic. They are classes that implement various tasks or functions that you want to perform. Think of services like distinct units in your application, each responsible for a specific type of job. Examples include:
EmailServicefor handling email-related tasks.NotificationServicefor sending notifications.InvoiceServicefor managing invoices.
In the context of workflows, services are primarily defined by their interfaces and are invoked using event-based RPC (Remote Procedure Call).
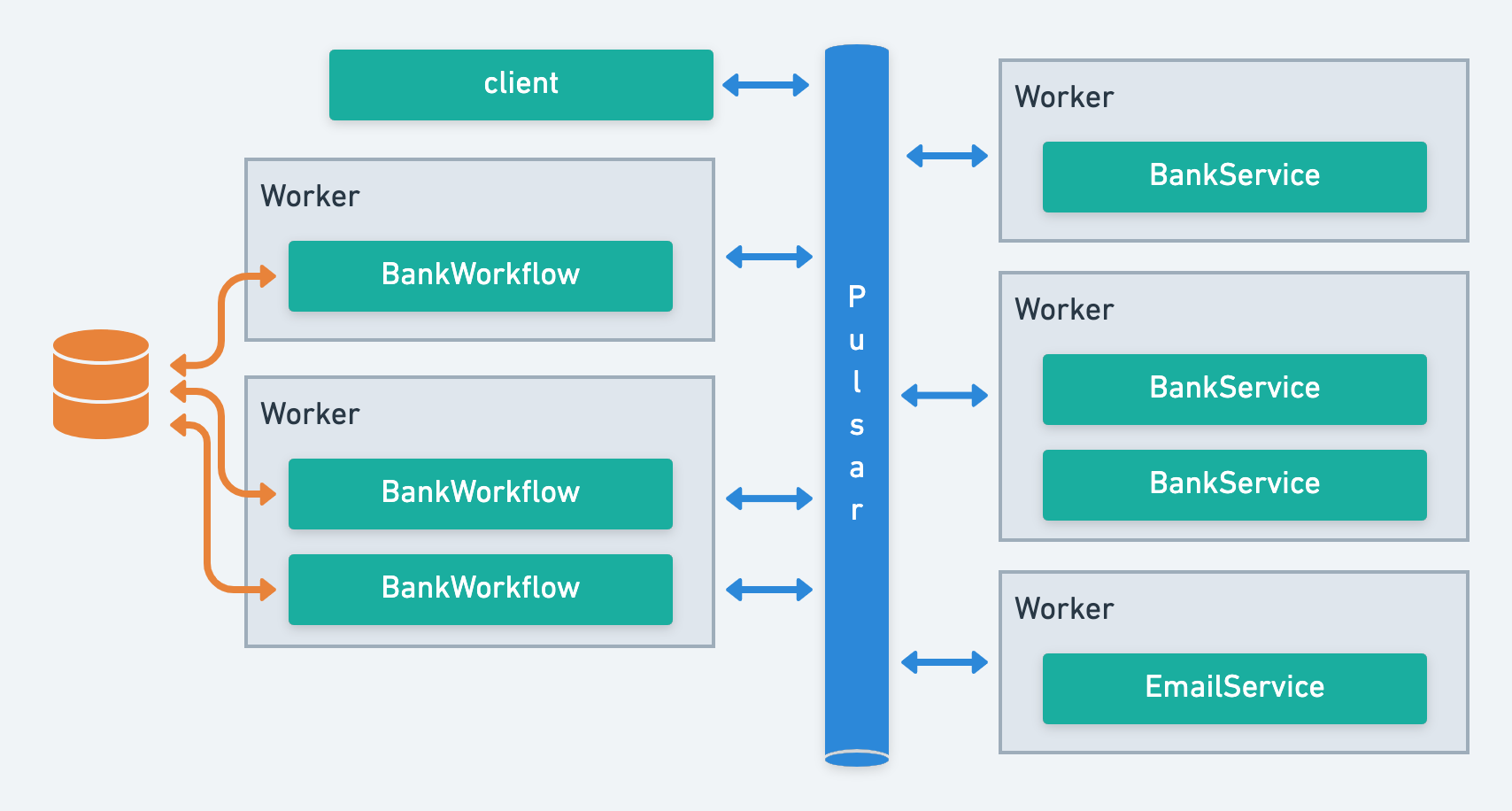
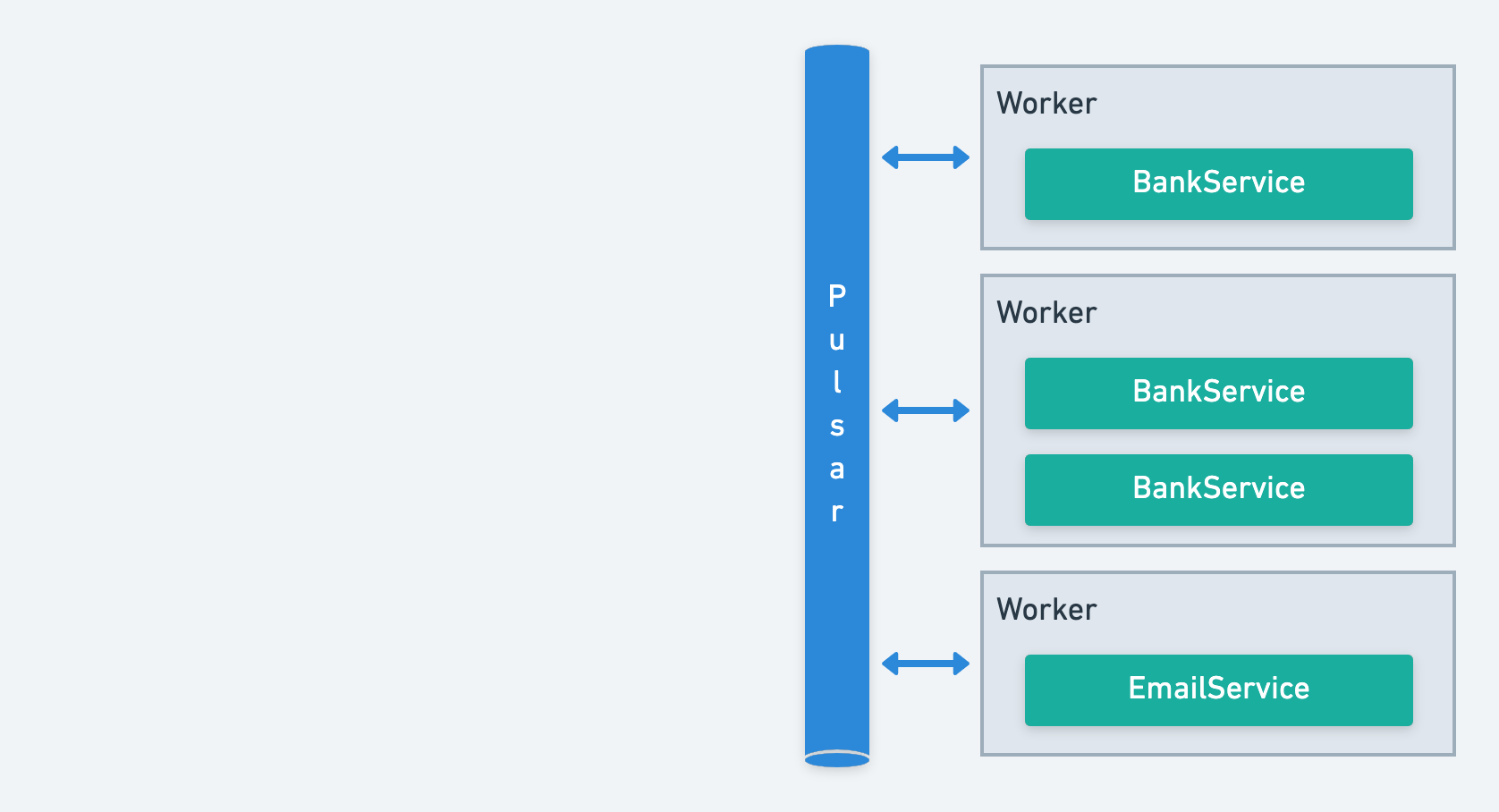
These services are implemented in classes within workers, which are connected and managed via the Apache Pulsar cluster. They can be scaled across multiple workers to handle parallel processing, ensuring efficiency and resilience.
Tasks
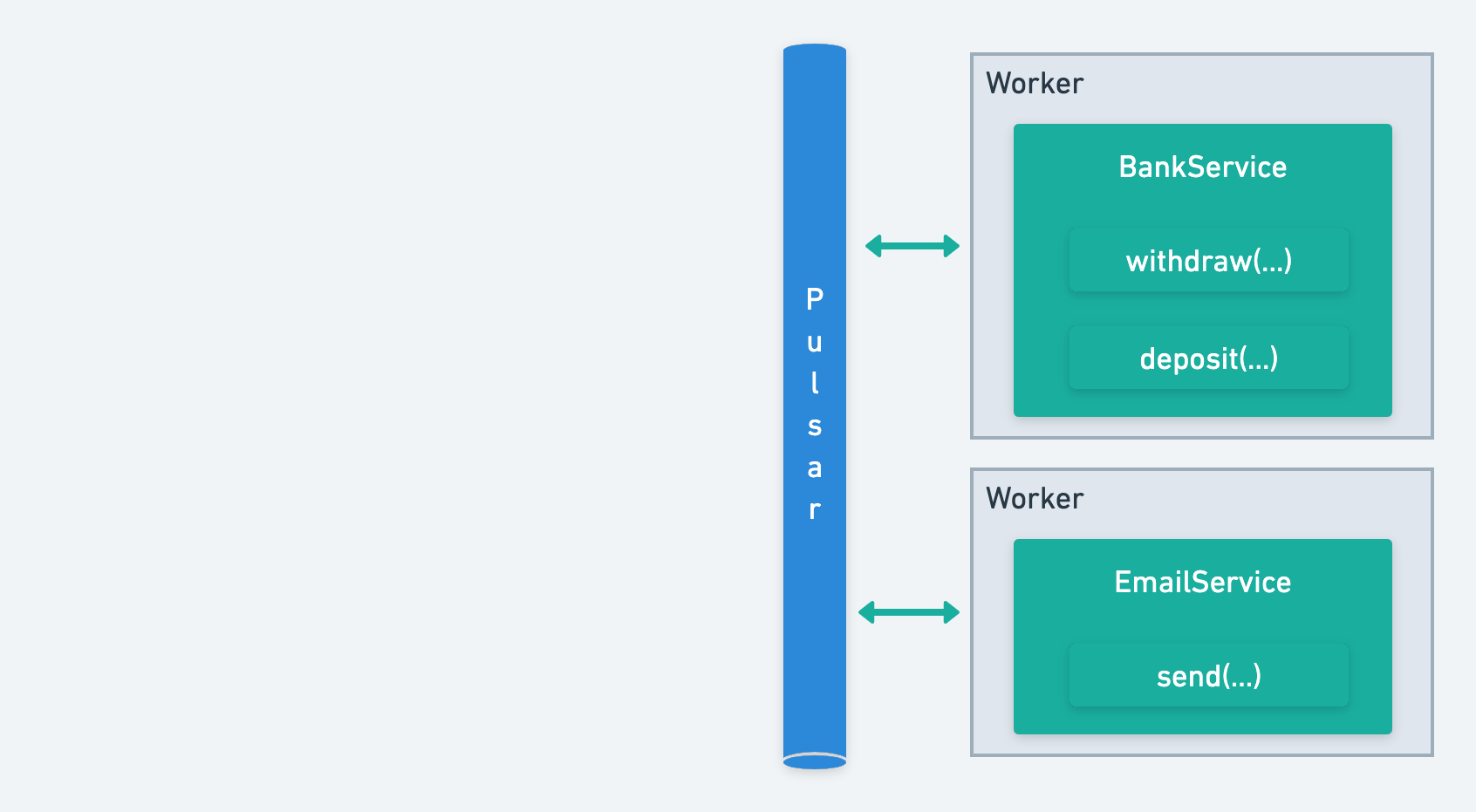
A task is essentially a method within a service class. It can be anything from a database operation, an API call, to any complex action specific to your domain. Tasks are processed inside workers and are invoked remotely via Apache Pulsar.
Workers
Workers are applications that run services. A worker embeds an Apache Pulsar's consumer listening the topics dedicated to each service it implements. When receiving the instruction to run a task, the worker deserializes the input, trigger the task procesing, and return the result to Pulsar in a JSON serialized format. Workers are stateless, meaning they don't store any data permanently, and can be scaled to meet demand. Workers also catch any task failure, and manage retries, ensuring that your distributed tasks are executed seamlessly.
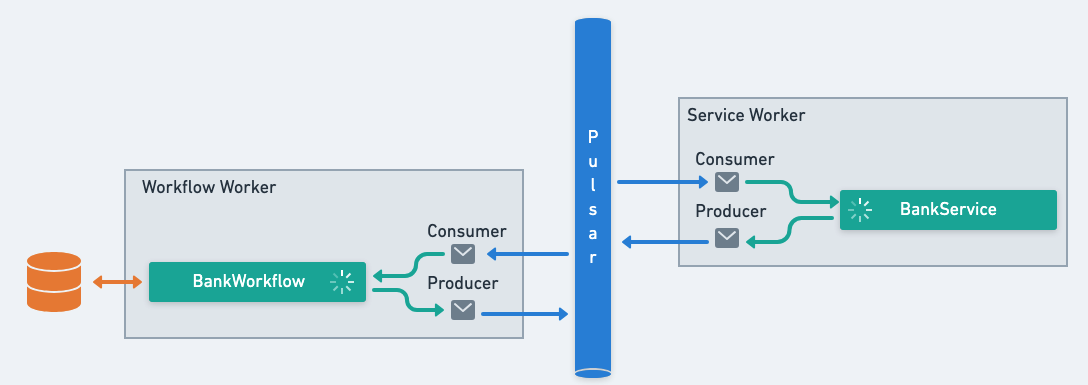
The complexity of communication between services and workflows is handled seamlessly for us. You don't have to worry about the underlying messages being sent back and forth.
In Infinitic, we use an orchestration pattern. This is different from a choreography pattern where services need to be aware of the events produced by other services. With orchestration, services are completely independent or decoupled. They don't need to know about each other's events; Infinitic coordinates everything.
Workflows
Workflows are special types of services that orchestrate the execution of various tasks. Unlike traditional methods, Infinitic workflows are defined using code, offering more flexibility and control.
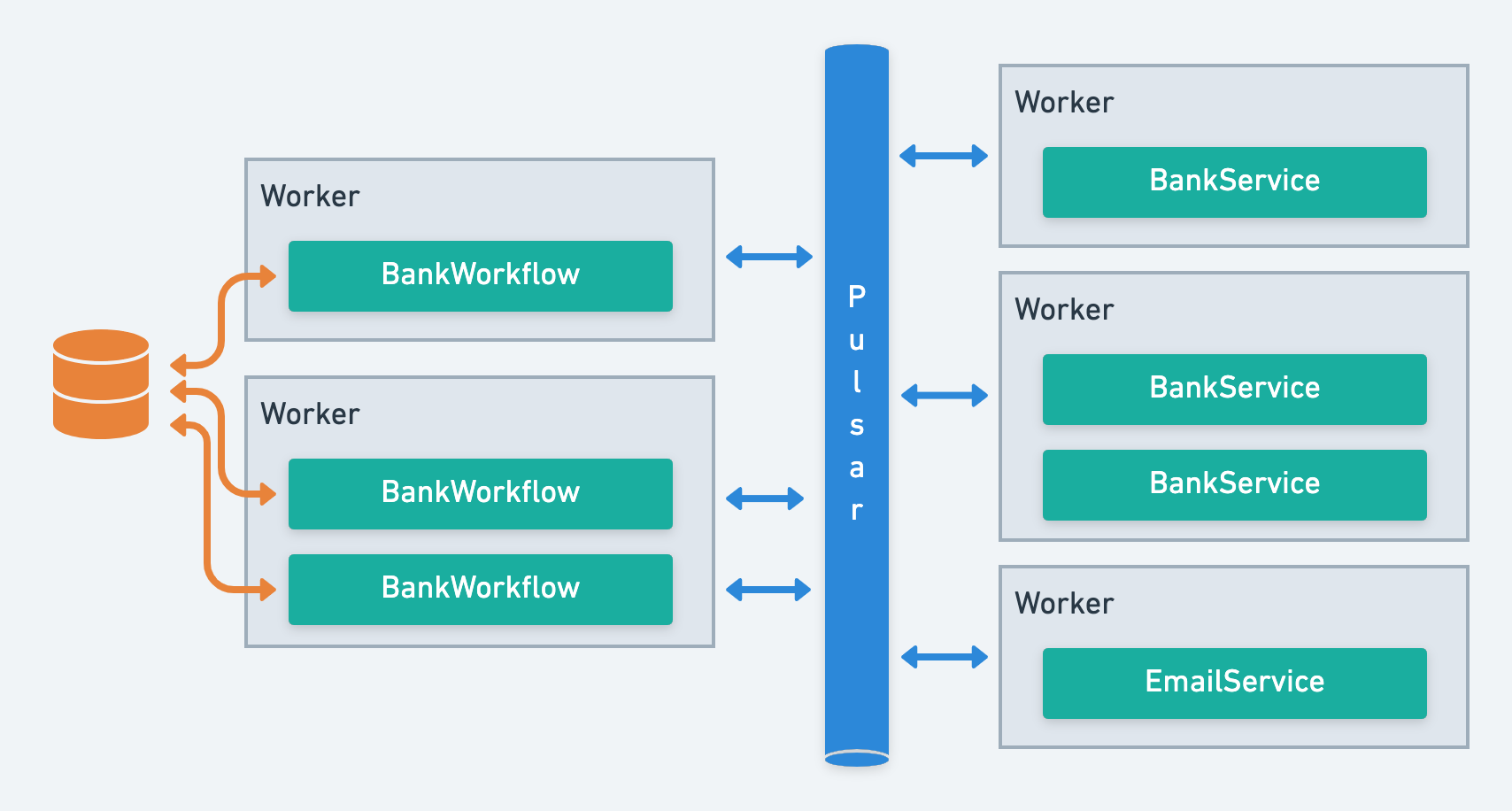
Workflow workers are also stateless and scalable. They connect to databases like Redis or MySQL to manage the state of each workflow instance, ensuring smooth progress and stateful execution.
Workflow services in Infinitic are managed differently compared to typical services. Each workflow consumer uses a method called a key-shared subscription, which is based on the workflow's ID. This approach is crucial for several reasons:
- Infinitic guarantees that messages pertaining to a particular workflow instance are handled sequentially. This orderly processing is crucial to prevent race conditions that could occur if multiple messages for the same workflow were handled simultaneously. Avoiding these situations is key to ensuring a predictable and stable task flow.
- Through the use of a key-shared subscription, a workflow service can receive all events linked to a specific workflow instance. This enables the service to keep a local cache of the workflow's state, reducing the need for frequent database queries.
- Finally, there's no requirement for techniques like database locking to avert race conditions during the saving of workflow states in the database. This aspect significantly enhances Infinitic's scalability, ensuring that the database doesn't become a performance bottleneck.
Clients
Client's Role. The client is primarily used to initiate new workflow instances. It needs to understand the workflow services' signatures and connect to the Apache Pulsar cluster to start and manage workflows.